Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hidaka, Akihide
Enerugi Rebyu, 35(9), p.20 - 24, 2015/09
Operation of nuclear power plant causes accumulation of radionuclides in fuel rods as a result of nuclear fission of uranium and plutonium. During severe accidents, large amount of radionuclides are released from fuel and transport in the reactor coolant system and/or the containment. When the containment fails or its confinement function is lost, radionuclides could be released into the environment. Meanwhile, radionuclides can be removed by condensation onto wall, natural deposition such as gravitational settling, the engineered safety features (ESF) such as containment spray and so on. After various processes described above, the species, amounts and timing of radionuclide released into the environment is called source terms. The behavior of radionuclide can be described mechanistically by condensation or evaporation of gaseous radionuclide, deposition, growth and removal of aerosol by ESF. Present paper summarizes the radionuclide behavior during severe accidents.
In, Teiji*; Shima, Shigeki*; Nakayama, Tomoharu*; Ishikawa, Yoichi*; Togawa, Orihiko; Kobayashi, Takuya; Kawamura, Hideyuki
Gekkan Kaiyo, 37(9), p.674 - 680, 2005/09
no abstracts in English
 Pb
Pb intermetallic compound
intermetallic compoundOno, Masao; Huang, X. S.*; Shibata, Yasuhiro*; Iguchi, Yusuke*; Sakai, Seiji; Maekawa, Masaki; Chen, Z. Q.*; Osakabe, Toyotaka; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 1st International Conference on Diffusion in Solids and Liquids (DSL 2005), p.531 - 533, 2005/07
Recently, we formed atomic-scale graded structures in some miscible alloys and observed the decomposition in Bi Pb
Pb intermetallic compound by sedimentation of atoms under strong gravitational field. In this study, we measured positron lifetime of centrifuged Bi
intermetallic compound by sedimentation of atoms under strong gravitational field. In this study, we measured positron lifetime of centrifuged Bi Pb
Pb , to which the composition change was very small as it was treated at low temperature. It was found that the positron lifetime became longer than that of starting state. This indicated that the point defects (vacancy or divacancy) increased in the sample by centrifugal treatment. We are now investigating the relationship between increase in point defects and sedimentation of atoms.
, to which the composition change was very small as it was treated at low temperature. It was found that the positron lifetime became longer than that of starting state. This indicated that the point defects (vacancy or divacancy) increased in the sample by centrifugal treatment. We are now investigating the relationship between increase in point defects and sedimentation of atoms.
Ono, Masao; Kinoshita, Takahiro*; Ueno, Hideto*; Huang, X.*; Osakabe, Toyotaka; Mashimo, Tsutomu
Materials Transactions, 46(2), p.219 - 224, 2005/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:54.84(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Ultracentrifuge experiments were performed on the In-Pb system to study the sedimentation of atoms and phase equilibrium. After the experiments, the graded structures were obtained. Pb-rich phase (f.c.c) and In-rich phase (tetragonal) appeared at the strong- and weak-gravitational field sides of the sample, respectively, from starting state of  -phase. And, the continuous changes in lattice parameters were observed in each phase. These observation results showed that the graded structure was continuous in atomic scale, and was formed by the sedimentation of atoms. Composition profiles of the centrifuged samples for 31.3 h, 60 h and 150 h showed that the composition change reached the steady state within 60 hours. The diffusion coefficient for sedimentation was estimated to be about 8 times larger than that for usual diffusion by the simulation. The result indicated that the diffusion mechanism of the sedimentation was different from the conventional ones.
-phase. And, the continuous changes in lattice parameters were observed in each phase. These observation results showed that the graded structure was continuous in atomic scale, and was formed by the sedimentation of atoms. Composition profiles of the centrifuged samples for 31.3 h, 60 h and 150 h showed that the composition change reached the steady state within 60 hours. The diffusion coefficient for sedimentation was estimated to be about 8 times larger than that for usual diffusion by the simulation. The result indicated that the diffusion mechanism of the sedimentation was different from the conventional ones.
Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Noriki, Shinichiro*
Journal of Oceanography, 61(1), p.25 - 40, 2005/01
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:50.74(Oceanography)Settling particles play an important role in transport of organic carbon from the surface to the deep ocean. It is known that major components of settling particles are biogenic silicates (opal), biogenic carbonate, lithogenic clays and organic matters. In this study, we estimated organic carbon fluxes that are carried by each component in the western North Pacific Ocean (WNP) including the Japan Sea. Mean organic carbon flux at 1 km depth in the WNP (13.5 mg/m /day) was larger than that in the Eastern North Pacific (7.4), central North Pacific (1.1), Equatorial Pacific (4.2), Southern Ocean (5.8) and Eastern North Pacific (1.8). In the WNP, opal was a dominant component and 55 % of particulate organic carbon was carried by opal particles. Opal is known as a major component even in the Eastern North Pacific and Southern Ocean and opal fluxes in these areas are as much as in the WNP. However, organic carbon flux that was carried by opal particles in the WNP was significantly larger than that in the Eastern North Pacific and the Southern Ocean. It was cleared that opal particles in the WNP had great abilities not only to activate the biological pump in the surface ocean but also to transport organic carbon to the deep ocean.
/day) was larger than that in the Eastern North Pacific (7.4), central North Pacific (1.1), Equatorial Pacific (4.2), Southern Ocean (5.8) and Eastern North Pacific (1.8). In the WNP, opal was a dominant component and 55 % of particulate organic carbon was carried by opal particles. Opal is known as a major component even in the Eastern North Pacific and Southern Ocean and opal fluxes in these areas are as much as in the WNP. However, organic carbon flux that was carried by opal particles in the WNP was significantly larger than that in the Eastern North Pacific and the Southern Ocean. It was cleared that opal particles in the WNP had great abilities not only to activate the biological pump in the surface ocean but also to transport organic carbon to the deep ocean.
Ono, Masao; Huang, X.*; Kinoshita, Takahiro*; Ueno, Hideto*; Osakabe, Toyotaka; Mashimo, Tsutomu
Defect and Diffusion Forum, 237-240(2), p.1101 - 1104, 2005/00
Ultra-strong gravitational field can induce sedimentation of even atoms in condensed matter. We had realized sedimentation of substitutional solute atoms in some miscible alloys. How about in the other alloys? So, In this study, the ultra-centrifuge experiments were performed on an intermetallic compound of Bi-Pb system (Bi Pb
Pb ) by changing time duration of experiment time (experimental conditions; maximum centrifugal force: 1.0
) by changing time duration of experiment time (experimental conditions; maximum centrifugal force: 1.0 10
10 g level, temperature: 130-150
g level, temperature: 130-150  C, duration: 30-150h, state: solid). Composition changes were observed in the centrifuged samples. And, it was found that the Bi phase appeared from starting state of Bi
C, duration: 30-150h, state: solid). Composition changes were observed in the centrifuged samples. And, it was found that the Bi phase appeared from starting state of Bi Pb
Pb around the weak gravitational field region of the sample. These results showed that sedimentation of substitutional solute atoms occurred, and induced the structure change in intermetallic compounds.
around the weak gravitational field region of the sample. These results showed that sedimentation of substitutional solute atoms occurred, and induced the structure change in intermetallic compounds.
Mashimo, Tsutomu
Defect and Diffusion Forum, 237-240(1), p.30 - 37, 2005/00
Mega-gravity field realizes the sedimentation of even atoms, and is expected to create a nonequilibrium crystal-chemical state in condensed matter. We presented a self-consistent diffusion equation for sedimentation of atoms in condensed matter. Next, we developed an ultracentrifuge to generate strong acceleration field of over 1 million g, and, recently, succeeded in realization of the sedimentation of substitutional solute atoms in some alloys. The diffusion coefficients of sedimentation on Bi-Sb alloy were estimated to be much greater than those of conventional one. It is suggested that the sedimentation of substitutional atoms in solids or liquids can be included in a new type of diffusion, where the diffusion mechanism was yet unknown. In this article, the recent progress in the investigation of sedimentation of atoms under mega-gravity field is reviewed, and the diffusion mechanism is discussed. The application of the mega-gravity field is also discussed.
Huang, X.*; Mashimo, Tsutomu; Ono, Masao; Tomita, Takeshi; Sawai, Tomotsugu; Osakabe, Toyotaka; Mori, Nobuo*
Journal of Applied Physics, 96(3), p.1336 - 1340, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:42.73(Physics, Applied)Mega-gravity field experiments were performed on the Bi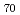 Sb
Sb (atomic percent) alloy and pure Bi below their melting points, to investigate the change in crystalline state. For the alloy centrifuged at 191-205
(atomic percent) alloy and pure Bi below their melting points, to investigate the change in crystalline state. For the alloy centrifuged at 191-205  C, no change in composition was observed, and the grain sizes of the crystals decreased from several mm to tens of
C, no change in composition was observed, and the grain sizes of the crystals decreased from several mm to tens of  m, while no distinct change in grain size was observed for the centrifuged pure Bi. The alloy centrifuged at 220-240
m, while no distinct change in grain size was observed for the centrifuged pure Bi. The alloy centrifuged at 220-240  C consisted of two regions with different morphologies-fine-grained crystals with grain sizes around tens of
C consisted of two regions with different morphologies-fine-grained crystals with grain sizes around tens of  m in the low gravity region, and large crystals with grain sizes several mm long and hundreds of
m in the low gravity region, and large crystals with grain sizes several mm long and hundreds of  m wide along the direction of gravity in the high gravity region, where sedimentation of atoms was confirmed. The large crystals with hexagonal structures were formed by preferential crystal growth roughly along the c axes, and a large strain that increased as the gravitational field increased existed inside these crystals. Formation of this anomalous crystal state might be correlated with the sedimentation of atoms.
m wide along the direction of gravity in the high gravity region, where sedimentation of atoms was confirmed. The large crystals with hexagonal structures were formed by preferential crystal growth roughly along the c axes, and a large strain that increased as the gravitational field increased existed inside these crystals. Formation of this anomalous crystal state might be correlated with the sedimentation of atoms.
 Pb in the northwestern Japan Sea
Pb in the northwestern Japan SeaOtosaka, Shigeyoshi; Baba, Masami*; Togawa, Orihiko; Karasev, E. V.*
Pacific Oceanography, 1(2), p.149 - 157, 2003/12
A sediment trap experiment and sediment coring were carried out in the northwestern Japan Sea (Sta MS), and lead-210 ( Pb) and major components in settling particles were measured. By drawing up a balance of
Pb) and major components in settling particles were measured. By drawing up a balance of  Pb in the water column, it was estimated that the cycle of
Pb in the water column, it was estimated that the cycle of  Pb in the Sta MS was controlled by 3 processes, (1) removal and vertical transport of
Pb in the Sta MS was controlled by 3 processes, (1) removal and vertical transport of  Pb from the surface layer by settling particles, (2) decomposition of particles in the deep layer, and (3) export by the deep current. Flux of
Pb from the surface layer by settling particles, (2) decomposition of particles in the deep layer, and (3) export by the deep current. Flux of  Pb at 3 km depth was large in winter and spring. The large
Pb at 3 km depth was large in winter and spring. The large  Pb flux in this season would be caused by the horizontal import of
Pb flux in this season would be caused by the horizontal import of  Pb -rich seawater from the coastal region to the bottom layer of Sta MS. It was suggested that seasonal variation of particulate
Pb -rich seawater from the coastal region to the bottom layer of Sta MS. It was suggested that seasonal variation of particulate  Pb flux at the deep layer in the northwestern Japan Basin indicated the renewal of the deep water in this area.
Pb flux at the deep layer in the northwestern Japan Basin indicated the renewal of the deep water in this area.
Mashimo, Tsutomu; Huang, X.; Osakabe, Toyotaka; Ono, Masao*; Nishihara, Masamichi*; Ihara, Hirotaka*; Sueyoshi, Masanori*; Shibasaki, Koji*; Shibasaki, Shiro*; Mori, Nobuo*
Review of Scientific Instruments, 74(1), p.160 - 163, 2003/01
Times Cited Count:54 Percentile:89.14(Instruments & Instrumentation)An ultracentrifuge apparatus, which could generate an ultra-strong gravitational field of even  1,000,000 (1 million) G (1G = 9.8 m/s
1,000,000 (1 million) G (1G = 9.8 m/s ) in a wide temperature range up to
) in a wide temperature range up to  500
500 C with high stability controls, was developed for new materials science research. The system consisted of an air turbine motor with ceramic ball bearings and dumper section, a sample rotor with an outer diameter up to 160 mm, a vacuum chamber and a heating system. The ultracentrifuge experiments using the 70 and 80 mm-diam rotors made of titanium alloy with rotational speeds of up to 170,000 rpm at temperatures of even over 200
C with high stability controls, was developed for new materials science research. The system consisted of an air turbine motor with ceramic ball bearings and dumper section, a sample rotor with an outer diameter up to 160 mm, a vacuum chamber and a heating system. The ultracentrifuge experiments using the 70 and 80 mm-diam rotors made of titanium alloy with rotational speeds of up to 170,000 rpm at temperatures of even over 200 C for 100 hours with the ripples of
C for 100 hours with the ripples of  0.05% and
0.05% and  1 degree, respectively, were successfully performed, where the maximum gravitational field at sample was
1 degree, respectively, were successfully performed, where the maximum gravitational field at sample was  1,000,000 G, and the potential energy and sample volume were larger than those of the Kumamoto University one (Rev. Sci. Instr. 67, 3170 (1996)) by
1,000,000 G, and the potential energy and sample volume were larger than those of the Kumamoto University one (Rev. Sci. Instr. 67, 3170 (1996)) by  1.9 and
1.9 and  4 times, respectively.
4 times, respectively.
Makino, Hitoshi; ; Miyahara, Kaname
JNC TN8400 2000-033, 74 Pages, 2000/11
Natural phenomena is one of the potential factors perturbing the long-term stability of the geological environment, and for natural phenomena, it is necessary to consider uncertainties relevant to time, frequency and effect. Therefore it will be important to have information about the potential impacts of natural phenomena on the safety functions of geological disposal system in the future by assuming that natural phenomena perturbs the safety functions of the geological disposal system. In this report, we have considered 4 natural phenomena, 'uplift, subsidence and denudation', 'climatic and sea-level changes', 'earthquakes and fault movement' and 'volcanism', which had been extracted by investigation in foreign countries and by considering the characteristics of Japan as natural phenomena which may perturb the long-term stability of the geological environment. And we have considered mainly typical effects of naturaI phenomena on geological environment and investigated the typical impacts of those natural phenomena on the safety functions of the geological disposal system. On perturbation scenarios, the maximum of total doses have been less than regulatory guidelines in foreign countries in all situations except the cases assuming that a new fault, which causes significant pathway of groundwater flow and nuclide migration, intersects the waste packages. In the case, the maximum of total doses may reach the same level as regulatory guidelines in foreign countries or natural radiation exposure in Japan depending on fault generation time or grandwater flow rate through the fault. And, on isolation failure scenarios, it has been implied that nuclide mass/flux originated from geological disposal is comparable level with nuclide mass/flux in natural environment. These results could give useful information about the potential impacts of natural phenomena on the safety functions of geological disposal system, and also could show the potential importance of ...
; ; Shimizu, Kazuhiko; Miyahara, Kaname; ; Hasegawa, Hiroshi; Makino, Hitoshi
JNC TN1400 99-007, 497 Pages, 1999/04
None
*; Fuse, Keisuke*; *; Yasuda, Kenya*
PNC TJ7454 97-001, 536 Pages, 1997/03
no abstracts in English
Takano, Toyoji*; Sasaki, Yutaka*; Fuse, Keisuke*; Saito, Akira*; Sato, Yoshikazu*
PNC TJ1454 96-001, 295 Pages, 1996/03
None
; ; Kawata, Tomio
PNC TN8410 92-012, 47 Pages, 1991/12
[Purpose] We confirmed that modified (6000rpm type) centrifugal clarifier arose the unstable vibration during the reduction of rotating speed under the condition of bearing undissolved residue after the clarification operation. This report describes the cause of unstable vibration that arise in the clarification body set on the rack which induced resonance vibration and the measurement results of vibration characteristic after taking countermeasure for vibration decrease. [Method] It was considered that the causes of the unstable vibration were following; (1)Unbalance between damping force of the lower bearing damper and the vibration force arisen by the rotational bowl (2)Effect of feed condition (3)Effect of self-excited vibration of the free liquid surface (4)Effect of frame strength The test has been conducted to make quantitative measure of vibration characteristic (amplitude of the rotational bowl and shaft) by changing the load in the rotational bowl. We also conducted the test to reconfirm the effect of the circumferential baffle plate which has shown the most effective effect to the vibration decrease in the preceding report. [Results] The effects of the circumferential baffle plate placed on the inside wall of the rotational bowl are shown as follows; (1)The unstable vibration during the reduction of rotating speed has been suppressed By this result, we verified that the vibration on the free liquid surface in the rotational bowl caused the vibration for the bowl without the circumferential baffle plate. (2)It was able to run the clarification operation in the standard condition(100 /h
/h  6h) for the rotational speed ranging from 4000 to 6000rpm. [Conclusion] By the results of this test and of the preceding report, the feed condition and the condition of setting the circumferential baffle plate are showed in the following, considering the aspects of rotational stability. (1)Condition of feed nozzle - feed 55㎜ in height from the lower ...
6h) for the rotational speed ranging from 4000 to 6000rpm. [Conclusion] By the results of this test and of the preceding report, the feed condition and the condition of setting the circumferential baffle plate are showed in the following, considering the aspects of rotational stability. (1)Condition of feed nozzle - feed 55㎜ in height from the lower ...
; Yasu, Takami; Kawata, Tomio
PNC TN8410 91-325, 68 Pages, 1991/11
[Purpose] We confirmed modified (6000rpm type) centrifugal clarifier happened unstable vibration in the downward rotation on the condition of including undissolved residue after the clarification operation. This report describes the cause of unstable vibration and the measurement results of vibration characteristic after taking countermeasure for vibration decrease. [Method] It was considered that the cause of unstable vibration was four items in the following. (1)Unbalance between damping force of lower bearing damper and vibration force arisen by rotational bowl (2)Effect of feed condition (3)Effect of self-excited vibration on the free surface (4)Effect of frame strength that be set modified. This test is for take countermeasure to each item (1 3 item) in the upper items, and for quantitative measure of vibration characteristic (amplitude of rotational bowl and shaft) in the downward rotation on the condition of including undissolved residue after the clarification operation and for select best countermeasure, that is most effective to vibration damping, and does not arise the fall of clarification performance (capture efficiency), the increase of leak rate of feed solution and the fall of sludge washing performance. [Results] (1)We could not confirme vibration damping, compared with spring constant k=9 kgf/cm, damping constant c=20㎏f
3 item) in the upper items, and for quantitative measure of vibration characteristic (amplitude of rotational bowl and shaft) in the downward rotation on the condition of including undissolved residue after the clarification operation and for select best countermeasure, that is most effective to vibration damping, and does not arise the fall of clarification performance (capture efficiency), the increase of leak rate of feed solution and the fall of sludge washing performance. [Results] (1)We could not confirme vibration damping, compared with spring constant k=9 kgf/cm, damping constant c=20㎏f s/cm and the former condition (k=600 kgf/cm, c=0.3 kgf
s/cm and the former condition (k=600 kgf/cm, c=0.3 kgf s/cm). (2)In case of countermeasure that operate as balance ring by sludge cohering height on the inside wall of rotational bowl, we could confirm that the amplitude in the downward rotation is about 1/3, the leak rate of feed solution is about 1/6, compared with the case of feed solution 55㎜ in height from the lower plate of rotational bowl and the former condition (25mm in height from the lower plate of rotational bowl). (3)Compared with the case of setting the side baffle plate 150㎜ in height from the lower plate of rotational bowl for decreasing ...
s/cm). (2)In case of countermeasure that operate as balance ring by sludge cohering height on the inside wall of rotational bowl, we could confirm that the amplitude in the downward rotation is about 1/3, the leak rate of feed solution is about 1/6, compared with the case of feed solution 55㎜ in height from the lower plate of rotational bowl and the former condition (25mm in height from the lower plate of rotational bowl). (3)Compared with the case of setting the side baffle plate 150㎜ in height from the lower plate of rotational bowl for decreasing ...
*; Muramatsu, Ken
CSNI-R-176, 13 Pages, 1991/00
no abstracts in English
Shinohara, Kunihiko*; *; Iwai, Makoto
PNC TN841 83-42, 74 Pages, 1983/05
no abstracts in English